The Role of AI in Modern Business Applications
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has moved from being an experimental technology to becoming a core driver of business transformation. According to recent research, 96% of global organizations have deployed AI models in some capacity. From customer service chatbots to predictive analytics in supply chains, AI is reshaping how businesses operate, compete, and innovate.
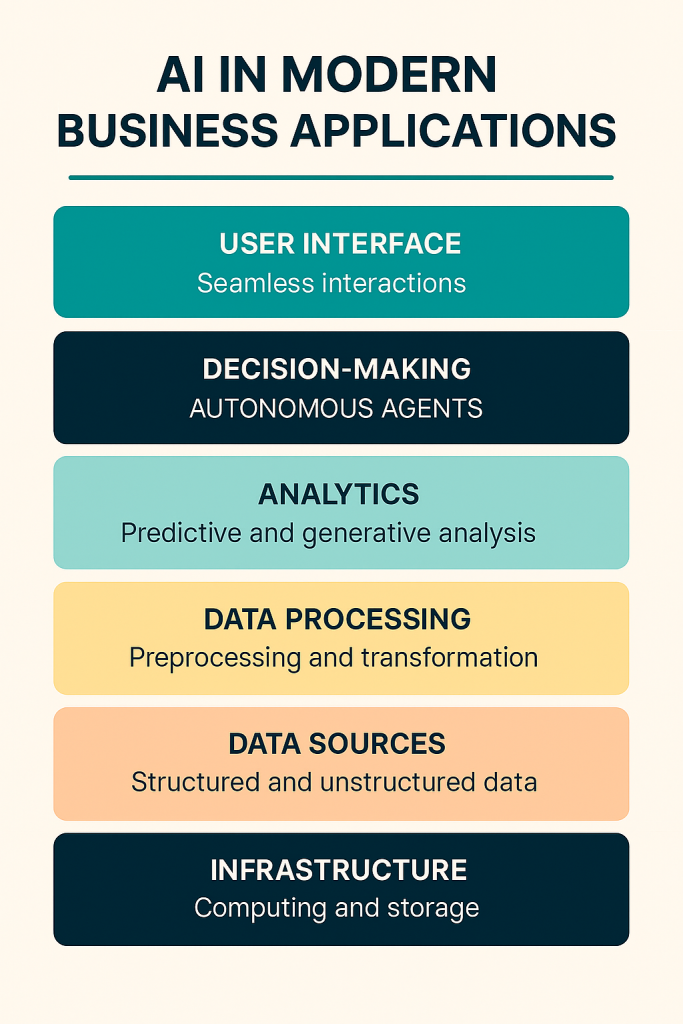
This article explores the current state of AI in business, its most impactful applications, the challenges organizations face, and the trends shaping its future.
1. Why AI Matters in Modern Business
AI enables organizations to process vast amounts of data, identify patterns, and make predictions faster and more accurately than traditional methods. This capability supports:
- Enhanced decision-making through predictive analytics and real-time insights
- Operational efficiency by automating repetitive tasks and optimizing workflows
- Customer experience improvements via personalization and conversational AI
- Innovation by enabling new products, services, and business models
The shift is not just technological but strategic. AI is now embedded in core business processes, influencing everything from marketing campaigns to risk management.
2. Key Applications of AI in Business
2.1 Customer Service and Experience
AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants use natural language processing (NLP) to handle routine queries, freeing human agents to focus on complex issues. Conversation analytics (CA) now goes beyond reactive insights, providing real-time sentiment analysis and enabling personalized interactions.
Example: AI-driven CA can detect customer frustration during a call and prompt an agent with tailored solutions.
2.2 Marketing and Sales
AI analyzes customer behavior to deliver hyper-personalized recommendations and optimize campaign targeting. Predictive models forecast buying patterns, enabling businesses to adjust strategies dynamically.
Example: E-commerce platforms use AI to recommend products based on browsing history, increasing conversion rates.
2.3 Supply Chain and Logistics
AI improves demand forecasting, inventory optimization, and route planning. McKinsey estimates AI applications in supply chains could generate up to $2 trillion in value.
Example: Generative AI tools allow supply chain managers to query systems in natural language for real-time insights on disruptions.
2.4 Financial Services
AI supports fraud detection, credit scoring, and algorithmic trading. Machine learning models identify anomalies in transaction data faster than manual reviews.
Example: Banks use AI to flag suspicious transactions in milliseconds, reducing fraud losses.
2.5 Cybersecurity and Application Security
AI enhances threat detection by identifying unusual patterns in network traffic. At Black Hat USA 2025, experts highlighted the need to secure AI-powered systems themselves, as they take on more autonomous roles.
Example: AI-driven CI/CD pipeline scanners detect vulnerabilities before deployment.
2.6 Hybrid Cloud and On-Device AI
While cloud-based AI offers scalability, it can introduce latency and cost challenges. Many organizations are adopting hybrid models or on-device AI to process data locally, improving speed and data sovereignty.
Example: On-device AI in laptops can summarize meetings without sending sensitive data to the cloud.
3. Benefits of AI in Business
- Speed and Scalability: AI processes data in real time, enabling faster decision-making.
- Cost Efficiency: Automation reduces labor costs and minimizes errors.
- Personalization: AI tailors experiences to individual customers, increasing loyalty.
- Risk Management: Predictive analytics helps anticipate and mitigate risks.
- Innovation Enablement: AI opens new possibilities for products and services.
4. Challenges and Risks
Despite its promise, AI adoption faces hurdles:
- Data Governance: Compliance with regulations like GDPR requires careful handling of sensitive data.
- Integration Complexity: Legacy systems and manual workflows can slow AI deployment.
- Security Risks: AI systems themselves can be targets for cyberattacks.
- Cost Management: Running large-scale AI models in the cloud can become expensive at scale.
- Skill Gaps: Many organizations lack in-house expertise to develop and maintain AI systems.
5. Future Trends
- Agentic AI: AI systems capable of autonomous decision-making will become more common, requiring new governance models.
- Hybrid AI Architectures: Combining cloud, on-premises, and edge AI to balance performance, cost, and compliance.
- Deeper Personalization: AI will integrate seamlessly into daily workflows, making interactions more intuitive.
- Responsible AI: Ethical frameworks and transparency will be critical to maintaining trust.
- Industry-Specific AI: Tailored AI solutions for sectors like energy, healthcare, and manufacturing will drive specialized innovation.
6. Conclusion
AI is no longer a futuristic concept but a present-day business imperative. Its role in modern business applications spans customer engagement, operational efficiency, risk management, and innovation. However, to unlock its full potential, organizations must address integration challenges, ensure robust governance, and align AI strategies with business goals.
The companies that succeed will be those that view AI not as a standalone tool but as an embedded capability that evolves alongside their operations.

Leave a Reply